The Moment Is Now
Enhance Your Brand: Enter the World of Forest Investment
Conviently Embrace the Rich Forest Opportunities Brazil Offers, Ensuring an Investment with a Substantial ROI and Protecting Yourself from Rising Carbon Credit Prices.
What Do I Buy.
Buying land in Brazil is not easy. Put your trust in reliable experts who have been trading farms for 30 years and are leaders in forest management.
Can I share the Risk?
Yes. Very often the deals are of such great interest or size that they arise to be divided among Investors. Whether they are International or Brazilian Investors.
What timing?
It depends on the status of the project in which you are interested. The Project must be submitted to and approved by VERRA. Development, project approval and Audit take time. We only propose projects whose Due Diligence has been successful, so the development time is certain.
Reliability
Having Standing Partners on the ground is everything.
Only a deep understanding of the market and its mechanisms make such interventions feasible.
The Marketplace
The Figures Speaking Plainly!
Trove Research’s exclusive and recent Report (September 2023) reveals impressive data:
📌 In the past 2.5 years, $18 billion in carbon credit funds have been raised or committed, and another $3 billion is already planned for 2024-2025.
📌 80 percent of this capital is allocated to nature-based projects such as reforestation and forest protection.
📌 Large global companies are investing to secure long-term access to carbon credits.
The point: current investment in carbon credit projects covers only one-third of the projected needs by 2030.
The opportunity is now! Make your move.
See the entire attached report and join the green wave of sustainable investing.

Carbon Sequestration: The Duel between REDD+ and ARR
Investing in both REDD+ and ARR projects has distinct advantages and challenges.
REDD+ Projects Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation:
- Economic Yield: They offer a high economic yield and are generally seen as short-term investments.
- Past Criticism: In the past, these projects have received criticism, mainly for the less stringent protocols adopted. However, the protocols for new REDD+ projects have been improved and are now well shielded from such criticism, ensuring both environmental and social integrity.
- More Widespread: REDD+ projects are more common and established in the carbon credits market.
ARR Projects Afforestation, Reforestation and Regeneration:
- Long-Term Investments: These are characterized by significant upfront costs due to reforestation. These costs can delay the economic break-even point of the project.
- Challenges with Landowners: Persuading a landowner to reforest an area potentially suitable for lucrative agricultural uses can be difficult. The remuneration required to compensate for the lost agricultural opportunity can be a significant additional cost.
- Environmental Benefits: They have direct environmental benefits, such as CO₂ capture through tree planting.
Assessing the specifics of each type of project, considering the maturity of the market, the speed of return on investment and the stability of the new protocols, it is suggested to opt for a REDD+ project. These projects, if managed properly following current protocols, can offer significant advantages in both environmental and economic terms over the ARR projects that are likely to become prevalent over time.
Why Choose Us
We listen to you
We find the Solution that Fits and Te
Due Diligence
IMPECCABLE project documentation
Standing
High profile.
Security
Administrative, Economic and Fiscal
Your Investment Path with Us
Choosing an investment project, especially in an international context such as Brazil, requires care, experience and specific knowledge of the area. Here is how we support you on this path:
- Identifying your needs: Our first priority is to understand your specific needs and expectations so that we can guide you to ideal solutions for you.
- Identification of achievable goals: Based on your needs, we map out a set of realistic and practically achievable goals.
- Presentation of a panel of offers: We provide you with a selection of projects that reflect your expectations, giving a comprehensive overview of the opportunities in the market.
- Legal Support: We introduce you to one of the most prestigious law firms in São Paulo, which will support you throughout the entire process, guaranteeing security and transparency.
- Operational Coaching: We connect you with our partner company in Brazil, experienced in project development, to ensure effective and timely implementation.
- Program Definition: Together we develop a detailed program of work and an accurate cash flow forecast, both in terms of investment and revenue.
- Scenarios and Trends: We provide you with an overview of possible scenarios, based on current and future market trends, so as to give you a clear view of potential returns.
- Business Outlets: We outline opportunities for selling Credits, giving a comprehensive view of available options.
- Partnership: If you wish, we can introduce you to possible partners with whom you can share the investment, to dilute any risks and maximize opportunities.
Perché Scegliere Noi?
Operating in Brazil can be complex, given its intricate legislation and the nature of local business relationships.
With us, you have access to stakeholders with deep industry knowledge and focus, and a high-profile international clientele.
While managing independently could lead to insurmountable challenges, our experience and network guarantee you a smooth and seamless path.
The complexity of projects involves working with numerous stakeholders, and we ensure efficient coordination among all parties, making the investment not only profitable but also stress-free.
What We Do.
The work done in Brazil is complex and multifaceted:
- Create, pre-diligate, negotiate and manage vast forest areas in the Amazon region for conservation projects.
- Connecting and advising landowners, investors, operators, and developers
- Advice for both buy-side and sell-side in M&A transactions involving agricultural and forestry companies
- Investing and divesting in cropland or greenfield properties-agriculture, planted forests, and native forests.
- Active participation in land creation for conservation projects to generate REDD+ and ARR carbon credits
- Search for farmland for temporary and permanent farming
- Structure of finance operations for accessing the capital market for financing agricultural and forestry projects
- Institutional relations that expedite government support, licensing, and infrastructure.
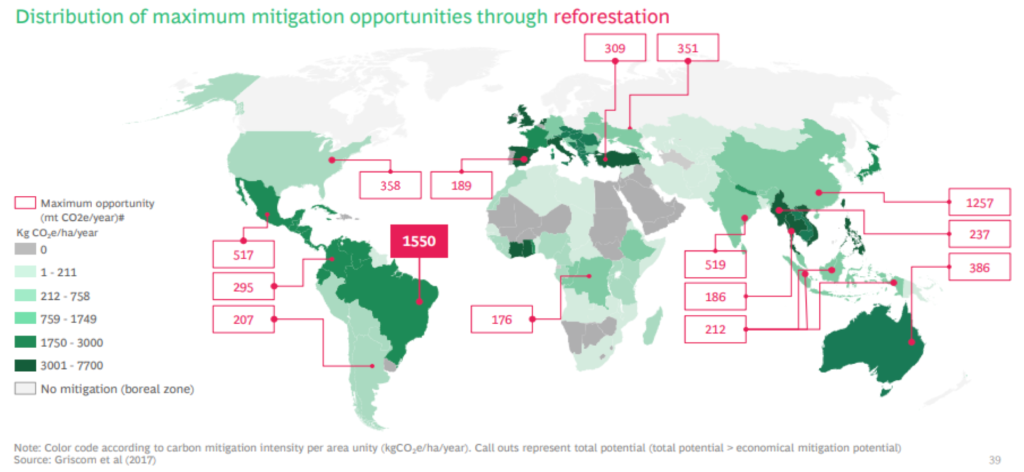
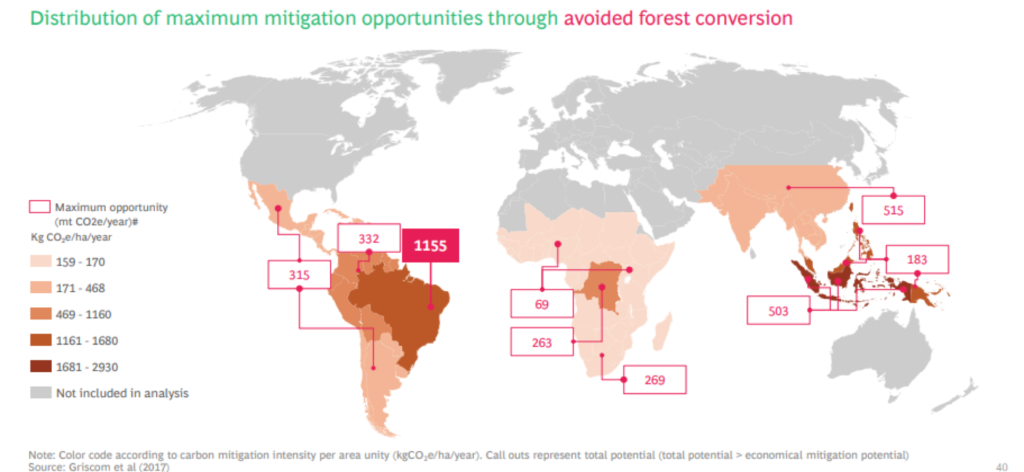
Where are the Projects ?
Brazil has by far the greatest potential for development of Forest Projects, especially in Standard ARR. Brazil is a large country and has the most suitable economic structure to effectively develop such projects and be able to guarantee their viability. Current efforts in the voluntary carbon market include 30 registered projects and 58 more in the pipeline. In total, this translates into as many as 34 million carbon credits per year.




Example: Macapà
ARR = Afforestation, Reforestation and Revegetation:
It is a project launched in the 2015, planting of 428,375 Eucalyptus trees.
It has removed more than 130,000 tons ofCO2.
FAQ
What REDD+ Means
REDD+ stands for “Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation More.” It is an approach designed to incentivize developing countries to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation and to promote conservation, sustainable forest management and increased forest stocks.
In essence, REDD+ aims to economically compensate countries that effectively reduce greenhouse gas emissions from deforestation and degradation of their forests. The goal is to use financial incentives to help conserve forests and contribute to the fight against climate change.
The “+” in REDD+ reflects the importance of going beyond just reducing emissions and also considering:
- Conservation of forest carbon stocks.
- Sustainable forest management.
- Increasing forest carbon stocks.
REDD+ has been formalized in international climate negotiations under the auspices of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and is one of the key tools to help countries achieve emission reduction targets and promote environmental sustainability.
What ARR means
In the context of carbon credits and sustainability, “ARR” stands for “Afforestation and Reforestation.”
Afforestation refers to the introduction of forests on land that has not been covered by forest for at least 50 years. Reforestation, on the other hand, refers to the resettlement of forest areas that have been deforested or degraded due to activities such as agriculture, timber extraction or natural disasters.
Under the carbon credit market, ARR projects can generate credits through the capture and storage of atmospheric carbon from planted or regenerated trees. These credits can then be sold or traded in various carbon markets around the world as part of global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Thus, an ARR certificate indicates that a certain amount of CO2 has been removed or avoided through afforestation or reforestation projects.
What AUD and APD mean
AUD – Avoided Unplanned Deforestation: This term refers to the prevention of deforestation that occurs in an unplanned way, such as due to sudden agricultural expansion or settlement. The goal is to protect areas of forest from unplanned activities.
APD – Avoided Planned Deforestation: Indicates the prevention of planned deforestation for activities such as commercial forestry or large-scale agricultural expansion. The intent is to modify or stop plans that involve logging.
What are the future forecasts for forestry projects
It is expected that the number of ARR projects will gradually increase in the future, becoming prevalent in carbon credits. However, it is crucial to consider that the complexity of developing an ARR project is significantly greater than other types of projects.
A landowner who has invested time and energy in converting land to pasture or cultivation may be reluctant to reforest it, given the perceived lower economic return. The financial valuation of land for agricultural production versus land for carbon credits may not immediately seem advantageous.
In addition, there are challenges related to climatic conditions: only certain geographical areas are suitable for reforestation, effectively limiting the areas in which to develop ARR projects. The choice of tree species for reforestation is another crucial aspect, since in order to meet the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the species chosen must be sustainable and suitable for the specific environment.
In summary, while there is growing potential for ARR projects, the inherent challenges require thorough planning and consideration to ensure their long-term success and sustainability.
Why REDD+ have a bad reputation
REDD+ credits are intended to incentivize forest conservation and thus reduce carbon emissions. However, over the years several concerns have emerged about this mechanism:
- Problems of Additionality: There were cases where forest areas protected by REDD+ were not actually threatened by deforestation. In such situations, no emission is effectively avoided.
- Beaching (leakage): While a forest area might be protected, deforestation activities might simply be moved to another area.
- Permanence: There is concern that forests protected today may be cut down in the future, releasing stored carbon again.
- Social Problems: There have been reports of indigenous and local communities being evicted or losing their traditional rights to land due to REDD+ projects.
- Double-counting: There is concern that emission reductions are counted by both the country hosting the REDD+ project and the entity (often a country or company) purchasing the carbon credit.
It should be noted that many of the most challenged projects are older ones, which used more permissive protocols. Through experience and criticism received, these protocols have been revised and tightened over time.
VERRA (Verified Carbon Standard) is an organization that seeks to address these and other concerns through rigorous standards and independent verification of emission reduction projects. Regarding REDD+, VERRA introduced the “VCS Jurisdictional and Nested REDD+” (JNR), a holistic approach that aims to integrate specific REDD+ projects within broader jurisdictional frameworks (often at the national or subnational level). This allows issues such as clearing to be addressed and ensures that avoided emissions are real and permanent.
In addition, VERRA is working with other organizations to ensure the participation of local and indigenous communities, to ensure that their rights are respected, and to promote social and environmental benefits beyond simply reducing carbon emissions.
Continued efforts to improve protocols and ensure fair and sustainable implementation of projects show that although there have been concerns related to REDD+, there is also great potential when they are implemented correctly.
